
Displacement velocity acceleration
tag:
Share:
Admin Koushi


SI unit of distance is meter (m) and dimension is [L].
SI unit of displacement is meter (m) and dimension is [L].
A particle moves in a circular path of radius r and comes to its initial position. The distance travelled by it is ![]() and displacement is zero.
and displacement is zero.
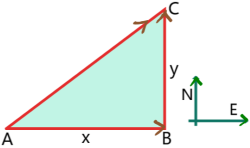
A particle moves in a straight path towards east for x unit and then towards north for y unit. The distance travelled by it is (x + y) and the displacement is ![]() .
.
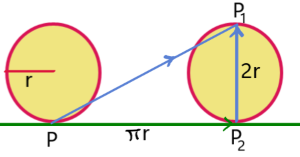
CONCEPT: A wheel of radius r rotates on a horizontal surface. Find the displacement of the point which touches the ground during half rotation.
Let us consider a point P of wheel touches the surface and after half rotation of the wheel that point (P) moves to ![]() and the point which touches the surface at that instant is
and the point which touches the surface at that instant is ![]() .
.
So, the horizontal displacement of the point P is ![]() and vertical displacement of the point P is
and vertical displacement of the point P is ![]() . So, net displacement of the point P is
. So, net displacement of the point P is ![]()
![]() .
.
Speed: The distance travelled by a particle per unit time is called speed. Speed is a scalar quantity. Speed = ![]() .
.
If s distance travelled by a particle in time t then speed of the particle is ![]() .
.
SI unit of speed is ms-1 and the dimension is [LT -1].
Uniform speed: A particle or a body is said to be moving with uniform speed, if it covers equal distance in equal interval of time.
Variable speed: A particle or a body is said to be moving with variable speed, if it covers unequal distance in equal interval of time.
Average speed: The average speed of a body is defined as the ratio of the total distance travelled by it to the total time taken.
If S1, S2, S3 are the distance travelled by a particle for time t1, t2, t3 respectively, then the average speed of it is ![]() .
.
Instantaneous speed: The instantaneous speed at a point is defined as the limit of the average speed over a path length that tends to become zero but always includes the point.
Let us consider a particle moves along a path ABCD and we want to calculate the instantaneous speed of it at point C. As the path ![]() s is very small, the corresponding time interval
s is very small, the corresponding time interval ![]() t also small.
t also small.
The instantaneous speed v is thus given by v = = ![]() .
.
Velocity: The displacement of a particle per unit time is called velocity. Velocity is a vector quantity. Velocity = ![]() .
.
If ![]() is the displacement of a particle in time t then velocity of the particle is
is the displacement of a particle in time t then velocity of the particle is ![]() .
.
SI unit of velocity is ms-1 and the dimension is [LT-1].
Uniform velocity: A particle or a body is said to be moving with uniform velocity, if it covers equal displacement in equal interval of time.
Variable velocity: A particle or a body is said to be moving with variable velocity, if it covers unequal displacement in equal interval of time.
Average velocity: The average velocity of a body is defined as the ratio of the total displacement travelled by it to the total time taken.
If ![]() are the displacement travelled by a particle for time t1, t2 respectively, then the average velocity of it is
are the displacement travelled by a particle for time t1, t2 respectively, then the average velocity of it is ![]() .
.
Instantaneous velocity: The instantaneous velocity at a point at a certain instant of time is the limit of the average velocity over a displacement that tends to zero but always includes the point.
The magnitude of the instantaneous velocity is the instantaneous speed and its direction is along the tangent to the path drawn at the corresponding point.
Let us consider a particle moves along a path ABCD and we want to calculate the instantaneous velocity of it at point C. As the displacement Δ![]() from point B to Dis very small, the corresponding time interval Δt also small.
from point B to Dis very small, the corresponding time interval Δt also small.
The instantaneous speed v is thus given by ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
SI unit of acceleration ms-2and the dimension is [LT-2].
CONCEPT: 2. The half of the distance travelled by a car with speed ![]() and the other half with speed
and the other half with speed ![]() . Calculate the average speed of the car.
. Calculate the average speed of the car.
Let us consider the total distance is 2x. Time for travelling the distance x with speed ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
Time for travelling the distance x with speed ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
The average speed of the car is ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Acceleration: The rate of increase of velocity of an object with time is called acceleration.
Acceleration = 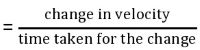
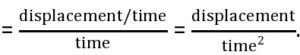 .
.
SI unit of acceleration ms-2and the dimension is [LT -2].
Retardation: The rate of decrease of velocity of an object with time is called retardation.
3. A train travels with uniform acceleration. When the front face of the train passes the electric post its speed is u and when the end face passes that post its speed is v. Calculate the speed of the train when the middle part of it passes that post.
Let the length of the train is L and acceleration is a. Then, ![]() or,
or, ![]() .
.
The speed of the train when the half part of it passes that post is w. So, ![]()
Or, ![]()
Or, ![]()
Or, ![]()
![]() .
.
© 2018 – 2025 Koushi All Rights Reserved