Mathematical tools and vector Class – IX
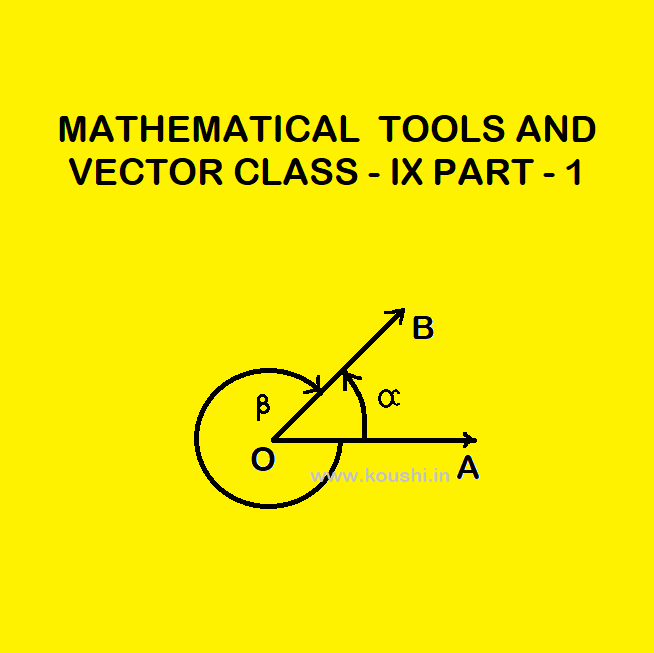
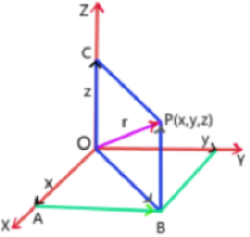
CONCEPT OF TRIGONOMETRY: Trigonometry is the part of mathematics where we learn about the angle. We know that in geometry the measured angle is restricted in between to and it is positive. But in trigonometry there is no limit of angle and it may be positive or negative. Let us consider OA and OB are […]
Mathematical tools and vector Class – IX Read More »