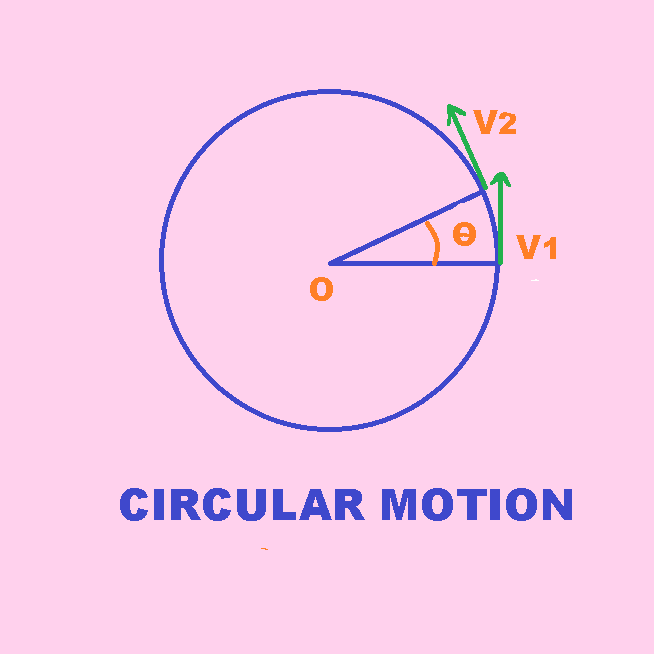
Circular motion:
Angular displacement: When a particle is in circular motion about an axis or centre, the angle described by the radius about the axis or centre is called angular displacement.
A particle rotates in a circular path of radius r about the centre O.
The particle moves from A to B through the circumference of the circle.
The angular displacement of the particle is ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]()
SI unit of angular displacement is radian. ![]() radian =
radian = ![]() .
.
Dimension of angular displacement ![]() or dimensionless.
or dimensionless.
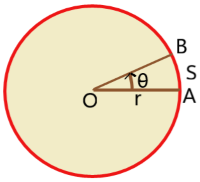
Angular speed: The angular displacement per unit time is called angular speed.
If ![]() is the angular displacement for time
is the angular displacement for time ![]() t then angular speed is
t then angular speed is ![]() [where
[where ![]() represents the small change.]
represents the small change.]
SI unit of angular speed is radian/second or ![]() .
.
Dimension of angular speed is ![]() .
.
Another unit of angular speed is revolution per minute (rpm) = 1rpm = ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
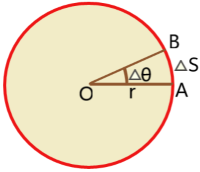
Time period: The time taken by the particle to complete one rotation is called time period.
Frequency: The number of full rotation completed by the particle in one second is called frequency.
So, Frequency = ![]() .
.
Relation between angular speed and time period: Angular speed ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
Relation between linear speed and angular speed: A particle rotates in a circular path of radius r about the centre O. The particle moves from A to B through the circumference of the circle.
The angular displacement of the particle is ![]() for time
for time ![]() t. Then angular speed is
t. Then angular speed is ![]() .
.
If the distance travelled by the particle is arc AB = ![]() then
then ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
So, ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]() [where linear speed v =
[where linear speed v = ![]() ]
]
![]() v =
v = ![]() .
.

Angular acceleration: The change of angular velocity per unit time is called angular acceleration.
If ![]()
![]() is the change of angular velocity for time
is the change of angular velocity for time ![]() then angular acceleration is
then angular acceleration is ![]() .
.
SI unit of angular acceleration is ![]() .
.
Dimension of angular acceleration is ![]() .
.
Relation between linear acceleration and angular acceleration: A particle rotates in a circular path of radius r about the centre O. The particle moves from A to B through the circumference of the circle for time ![]() .
.
The change of angular velocity of the particle from A to B is ![]()
![]() . Then angular acceleration is
. Then angular acceleration is ![]() .
.
If ![]() is the change in linear velocity of the particle from A to B then linear acceleration
is the change in linear velocity of the particle from A to B then linear acceleration ![]() [as v = r
[as v = r![]() so,
so, ![]() = r
= r![]()
![]() where r is constant].
where r is constant].
So, a = r![]() .
.
Video explanation of this post.