
Refraction Class – X Part – 3
- By Admin Koushi
- (2) comments
- June 26, 2025
Refraction Class – X Part – 3
Bending of an immersed object: Let us consider a rod AB is dipped in water. The portion OB of the rod dipped in water appears to be shortened and raised up as OC. The rays of light from point B bend away from the normal after refraction at the interface separating the air and water. These refracted rays appear to come from point C. So the OB portion of the rod appears to OC. For this reason the object immersed in liquid appears to bend.

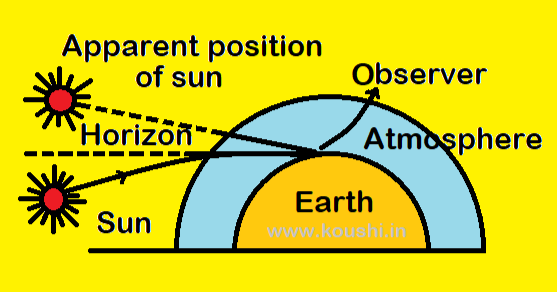
Time difference during sunrise and sunset: Sun is visible to an observer after the actual sunset because of refraction of light due to denser atmosphere near the earth. The apparent shift in the direction of sun is about 0.50 leading to delay of 2 minute in actual and apparent sun set. Time taken for 3600 shift of sun is 24 hours. So time taken for 0.50 shift is ![]() = 2 minutes
= 2 minutes
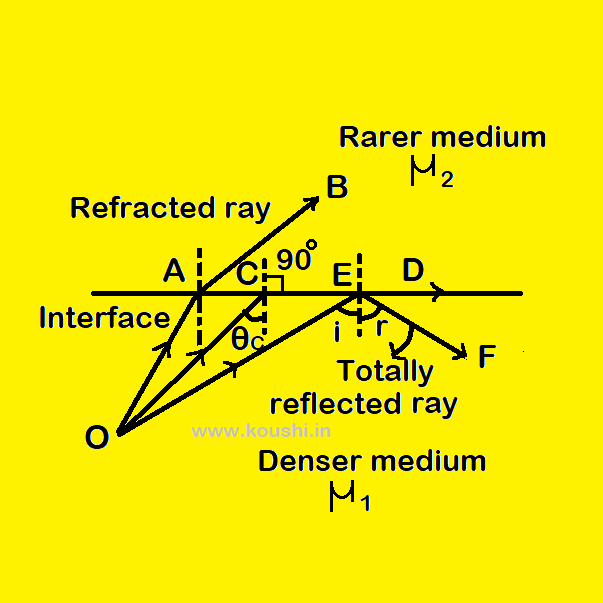
Critical angle: When light travels from denser medium to rarer medium, for a specific angle of incidence, angle of refraction is 900. So the refracted light passes through the interface of the medium. That angle of incidence is called critical angle.
Relation between refractive index and critical angle: When a ray of light travels from denser medium (say 1) to rarer medium (say 2), for the angle of incidence θc the angle of refraction is 900. So using Snell’s law ![]() = 1µ2
= 1µ2
Or, sin ![]() =
= ![]() ——(1). If medium 2 is air then µ2 = 1 and µ1 = µ (say), then from equation (1) we get, sin
——(1). If medium 2 is air then µ2 = 1 and µ1 = µ (say), then from equation (1) we get, sin ![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() = sin-1(
= sin-1(![]() ).
).
Total internal reflection: The phenomenon of reflection of light when a ray of light travelling from denser medium to rarer medium is sent back to the same denser medium provided it strikes the interface of the denser and the rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle is called total internal reflection. As there is no light is absorbed in rarer medium, so intensity of reflected light is 100%.
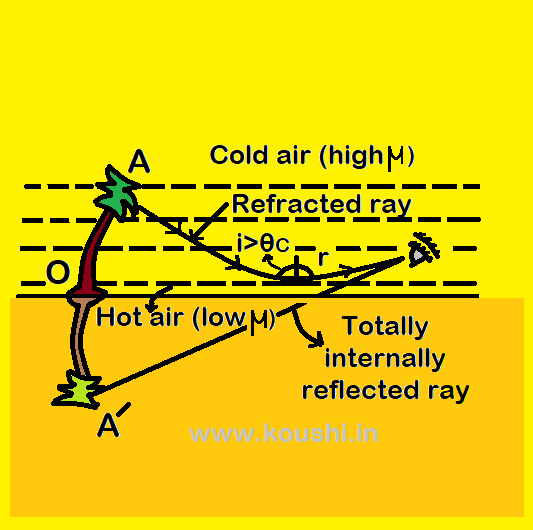
Mirage: When people travelling through desert sometimes they see water at a distant place which is actually an optical illusion, this is known as mirage. Due to sunlight the upper surface of desert becomes hot and this heat transfer to the lower region of atmosphere. Therefore the optical density of air in the lower region is less than that of in the higher region.
Whenever light passes through the different layers of atmosphere, it travels from denser medium to rarer medium. At a particular layer of atmosphere, whenever the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle (![]() ) of that medium then total internal reflection takes place and light travels back from that medium. The totally internally reflected ray travels from rarer medium to denser medium and refraction takes place. After multiple refraction, this ray is received by an observer and he gets an inverted virtual image at different position. Due to continuous change in temperature, all the layers undergoes continuous change in density and hence the refractive index as well as the path of rays coming through the layers are also continuously changing. Hence the observer imagine that the image appears to be swaying. This completes the illusion of a pond with trees and the observer moves towards that image and diverts his path.
) of that medium then total internal reflection takes place and light travels back from that medium. The totally internally reflected ray travels from rarer medium to denser medium and refraction takes place. After multiple refraction, this ray is received by an observer and he gets an inverted virtual image at different position. Due to continuous change in temperature, all the layers undergoes continuous change in density and hence the refractive index as well as the path of rays coming through the layers are also continuously changing. Hence the observer imagine that the image appears to be swaying. This completes the illusion of a pond with trees and the observer moves towards that image and diverts his path.
Sparkling of diamond: Sparkling of diamond is based on the total internal refraction. The refractive index of diamond is nearly 2.42 and its critical angle relative to air is nearly for 24.50. Diamonds are skilfully cut with many faces in such a way that much of the incident light undergoes multiple total internal reflection within the diamond before passing out in air again. Diamond also have dispersive property, so various colour of light travels in different paths and emerge in different directions.

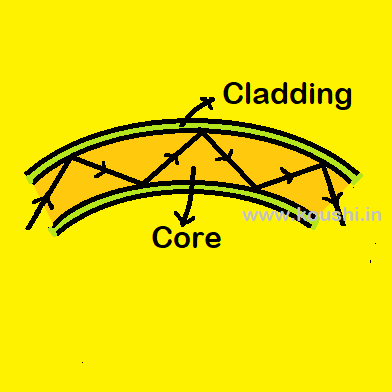
Optical fibre: Optical fibre is a glass rod (called core) with small radius (radius of few micron) is coated with a thin layer of material of refractive index less than that of core. The coating of surrounding layer is called cladding. When light falls at one end of the optical fibre, it gets refracted into the fibre the refracted ray falls on the interface of core and cladding at an angle which is greater than the critical angle. Therefore total internal reflection takes place and light travels the entire length of the fibre and arrives at the other end without any loss of intensity. Optical fibre is used to transmit light, it is also used in endoscopy, telecommunication system etc.
Click the button to go the previous part of this chapter.


2 Comments
Howdy very nice site!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb
.. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionally?
I’m happy to search out so many useful information here
within the submit, we need work out extra strategies on this
regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
casino en ligne fiable
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this post and the rest of the website is extremely
good.
casino en ligne francais
Can you tell us more about this? I’d like to find out some additional information.
casino en ligne
Hey there would you mind letting me know which web host you’re
utilizing? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different web browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most.
Can you suggest a good internet hosting provider at a honest price?
Cheers, I appreciate it!
meilleur casino en ligne
Hi there, I found your web site by way of Google while looking for a
related matter, your web site got here up, it seems to be great.
I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks. Hello there, simply changed into aware of your blog thru Google,
and found that it is truly informative. I’m going
to be careful for brussels. I will appreciate for those who continue this
in future. Numerous other people will be benefited out of your writing.
Cheers!
meilleur casino en ligne
Good day! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a team of volunteers
and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche.
Your blog provided us beneficial information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
casino en ligne fiable
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article.
Many thanks for supplying these details.
casino en ligne
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts.
After all I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope
you write again soon!
casino en ligne fiable
It’s actually a cool and helpful piece of
information. I’m happy that you simply shared this helpful information with us.
Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
casino en ligne
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post
is written by him as nobody else know such detailed
about my trouble. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
casino en ligne
Thanks for visit my site.