
Work Energy Power Part 3
tag:
Share:
Admin Koushi


Work done by static friction: When static friction is acting between body and the surface, then there is no relative displacement between body and surface. Therefore static friction doesn’t perform any work.
If a body is placed on a rough surface and force is applied on the body and we have to calculate the work done by the force, then at first calculate the value of limiting friction. If the value of limiting friction is greater than the applied force, it signifies that there is no relative displacement between body and the surface. Therefore, the work done by the force on the body is zero.
Example: A block of mass M is placed on a smooth surface and another block of mass m is placed on M. F force is applied on M for time t as shown in figure. We assume that frictional force acts between two blocks and there is no relative displacement between them. Calculate work done by static friction on blocks. Calculate work done by the external force.
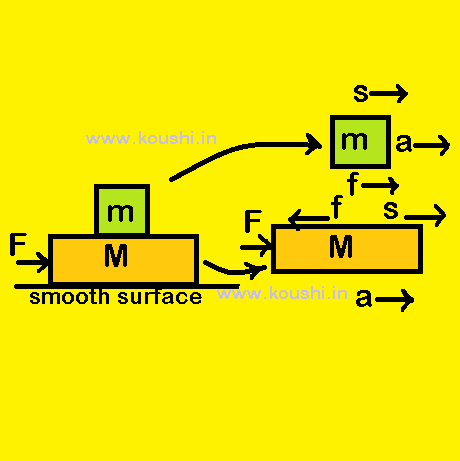
As there is no relative displacement between two blocks and the horizontal surface is smooth, then two blocks will move with same acceleration a = ![]() .
.
The value of limiting friction fs = ma = ![]() .
.
As F force is applied on block M towards right, therefore static friction applied by m on M acts towards left. Similarly static friction applied by M on m is towards right.
The displacement of blocks for time t is s = ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
The work done by static friction on M is WM = -fs.s = – ![]() . [Displacement and friction is in opposite direction]
. [Displacement and friction is in opposite direction]
The work done by static friction on m is Wm = fs.s = ![]() . [Displacement and friction is in same direction]
. [Displacement and friction is in same direction]
Net work done by static friction is W = WM + Wm = -fs.s + fs.s = 0.
Work done by the external force is WF = Fs = ![]() .
.
Work done by kinetic friction: When a body slides over a rough surface then there is a relative displacement between the surface and the body and kinetic friction acts between the body and the surface. Therefore, kinetic friction performs work.
If fk is the kinetic friction acting on the body opposite to the displacement s, then work done by the friction on the body is W = – fks.
If the surface is fixed, then work done by the friction on the surface is zero.
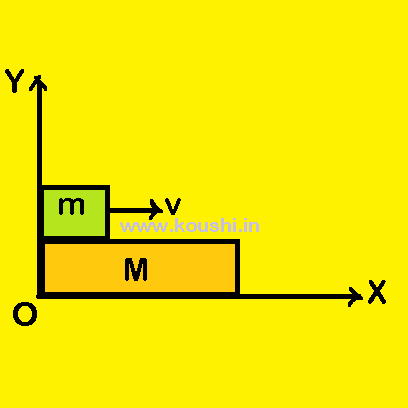
Work done by the kinetic friction when a body is moved on a movable surface: Let us consider a block of mass m is placed on a plank of mass M as shown in figure.
Friction acts between the body and the plank. The surface on which the plank is placed is smooth.
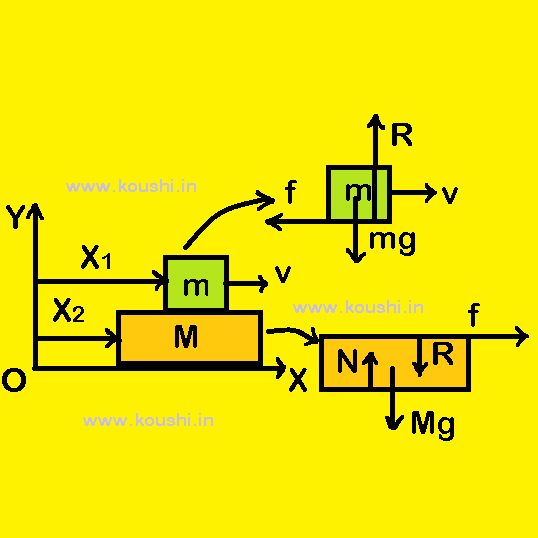
Initially the block is moving with speed v relative to the plank and slide a distance x relative to the plank. fk is the kinetic friction acts on the block by plank towards left and the block moves a distance x1. The work done by the friction on block is WB = -fkx1.
Friction applied by block on plank is towards right and displacement of plank x2 is also towards right. Therefore the work done by the friction on plank is WP = fkx2.
The total work done by the frictional force is W = WB + WP = -fkx1+ fkx2 = – fk(x1 – x2) = -fkx.
Example: A block of mass m is moved on a rough horizontal surface with constant speed by applying force at an angle 600 with vertical. The coefficient of friction between surface and block is ![]() . Find the work done to move the block for a distance s on the surface.
. Find the work done to move the block for a distance s on the surface.
Let us consider F force is applied on the body. The horizontal component of applied force is Fsin600 = ![]() .
.
As the body is moved with constant speed then, horizontal component of applied force = frictional force
Or, ![]() =
= ![]() R
R
Or, ![]() =
= ![]() (mg – Fcos600)
(mg – Fcos600)
Or, ![]() =
= ![]() (mg –
(mg – ![]() )
)
Or, ![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]() mg
mg
![]() F =
F = ![]()
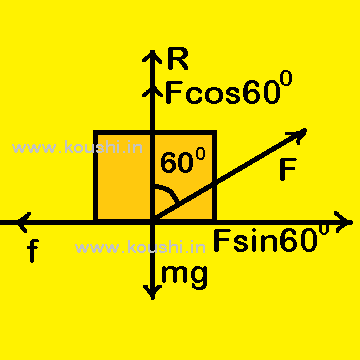
The work done to move the body for a distance s on the surface is w = horizontal component of applied force ![]() distance travelled
distance travelled
![]() w =
w = ![]() .s =
.s = ![]() (
(![]() ) =
) = ![]() .
.
© 2018 – 2025 Koushi All Rights Reserved