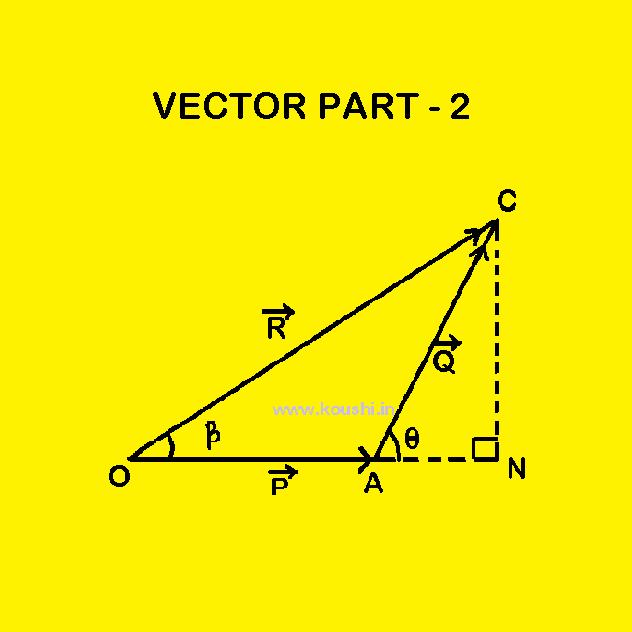
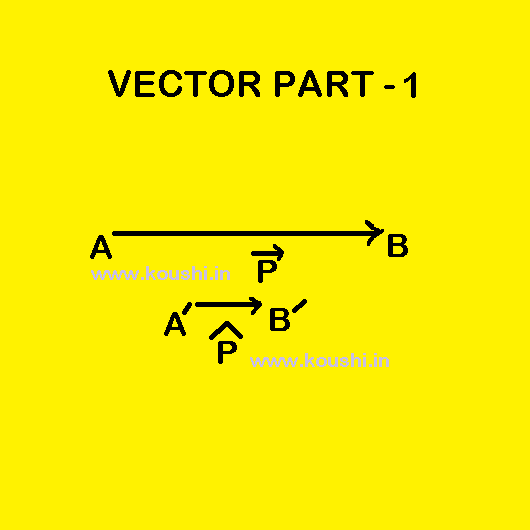
Vector Part 6
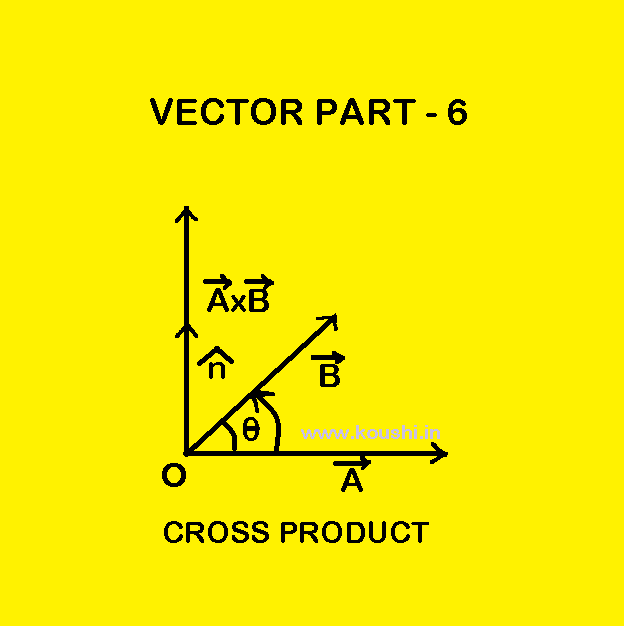
Vector product or cross product: The vector product of two vectors and is defined as the product of the magnitudes of and and the sine of the angle between them. If and creates angle θ then = AB. Where is the unit vector perpendicular to the plane of and . Properties of cross product: = […]