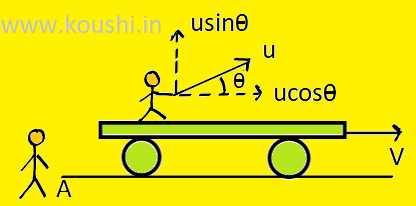
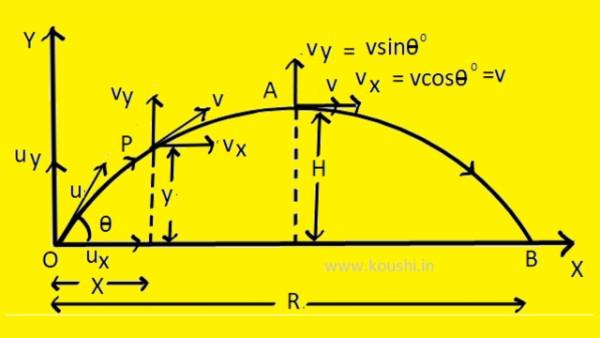
Gravitation
Kepler’s law of planetary motion: 1) All planets revolve around sun in elliptical orbit and the sun situated at any one foci of that ellipse. 2) The speed of planet varies in such a way that the radius vector drawn from the sun to a planet sweeps out equal area in equal interval of time. […]
Explore More