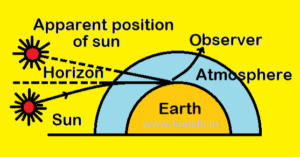
Time difference during sunrise and sunset: Sun is visible to an observer after the actual sunset because of refraction of light due to denser atmosphere near the earth. The apparent shift in the direction of sun is about 0.50 leading to delay of 2 minute in actual and apparent sun set. Time taken for 3600 shift of sun is 24 hours. So time taken for 0.50 shift is ![]() = 2 minutes
= 2 minutes
Critical angle: When light travels from denser medium to rarer medium, for a specific angle of incidence, angle of refraction is 900. So the refracted light passes through the interface of the medium. That angle of incidence is called critical angle.
Relation between refractive index and critical angle: When a ray of light travels from denser medium (say 1) to rarer medium (say 2), for the angle of incidence θc the angle of refraction is 900. So using Snell’s law ![]() = 1µ2
= 1µ2
Or, sin ![]() =
= ![]() ——(1). If medium 2 is air then µ2 = 1 and µ1 = µ (say), then from equation (1) we get, sin
——(1). If medium 2 is air then µ2 = 1 and µ1 = µ (say), then from equation (1) we get, sin ![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() = sin-1(
= sin-1(![]() ).
).
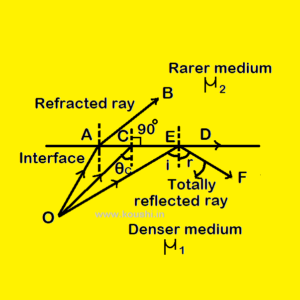
Total internal reflection: The phenomenon of reflection of light when a ray of light travelling from denser medium to rarer medium is sent back to the same denser medium provided it strikes the interface of the denser and the rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle is called total internal reflection. As there is no light is absorbed in rarer medium, so intensity of reflected light is 100%.
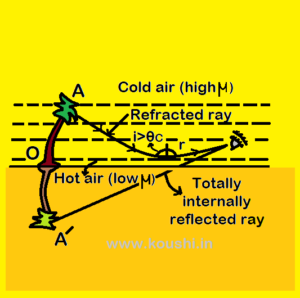
Mirage: When people travelling through desert sometimes they see water at a distant place which is actually an optical illusion, this is known as mirage. Due to sunlight the upper surface of desert becomes hot and this heat transfer to the lower region of atmosphere. Therefore the optical density of air in the lower region is less than that of in the higher region.
Whenever light passes through the different layers of atmosphere, it travels from denser medium to rarer medium. At a particular layer of atmosphere, whenever the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle (![]() ) of that medium then total internal reflection takes place and light travels back from that medium. The totally internally reflected ray travels from rarer medium to denser medium and refraction takes place. After multiple refraction, this ray is received by an observer and he gets an inverted virtual image at different position. Due to continuous change in temperature, all the layers undergoes continuous change in density and hence the refractive index as well as the path of rays coming through the layers are also continuously changing. Hence the observer imagine that the image appears to be swaying. This completes the illusion of a pond with trees and the observer moves towards that image and diverts his path.
) of that medium then total internal reflection takes place and light travels back from that medium. The totally internally reflected ray travels from rarer medium to denser medium and refraction takes place. After multiple refraction, this ray is received by an observer and he gets an inverted virtual image at different position. Due to continuous change in temperature, all the layers undergoes continuous change in density and hence the refractive index as well as the path of rays coming through the layers are also continuously changing. Hence the observer imagine that the image appears to be swaying. This completes the illusion of a pond with trees and the observer moves towards that image and diverts his path.
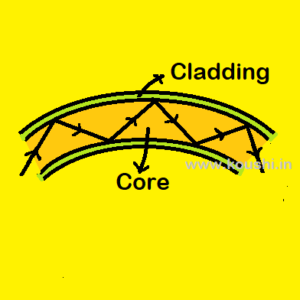
Optical fibre: Optical fibre is a glass rod (called core) with small radius (radius of few micron) is coated with a thin layer of material of refractive index less than that of core. The coating of surrounding layer is called cladding. When light falls at one end of the optical fibre, it gets refracted into the fibre the refracted ray falls on the interface of core and cladding at an angle which is greater than the critical angle. Therefore total internal reflection takes place and light travels the entire length of the fibre and arrives at the other end without any loss of intensity. Optical fibre is used to transmit light, it is also used in endoscopy, telecommunication system etc.
Example: 1. A glass cube has refractive index ![]() . A glass plate of refractive index
. A glass plate of refractive index ![]() (
(![]() >
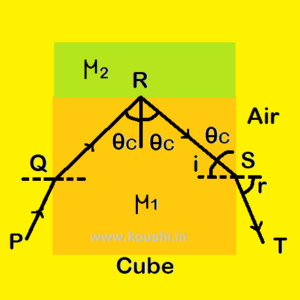
> ![]() ) is placed above the cube. A ray of light is travelling through air is incident on a side face of the cube. The refracted ray is incident on the upper face of the cube at the minimum angle for total internal reflection to occur. Finally the reflected ray emerges from the opposite face. Find the value of angle of emergence.
) is placed above the cube. A ray of light is travelling through air is incident on a side face of the cube. The refracted ray is incident on the upper face of the cube at the minimum angle for total internal reflection to occur. Finally the reflected ray emerges from the opposite face. Find the value of angle of emergence.
PQ is the incident ray on the side face of the cube. QR is the refracted ray inside the cube and RS is the totally reflected ray from the upper surface of the cube. ST is the emergent ray from the opposite face of the cube and r is the angle of emergence.
If ![]() is the critical angle of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 then = 1µ2 =
is the critical angle of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 then = 1µ2 = ![]()
Or, sin ![]() =
= ![]()
At point S, i = 900 – ![]()
Using Snell’s law at point S we get, ![]() = 1µa =
= 1µa = ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, sin r = ![]()
Or, sin r = ![]()
Or, sin r = ![]()
![]() r = sin-1
r = sin-1![]()
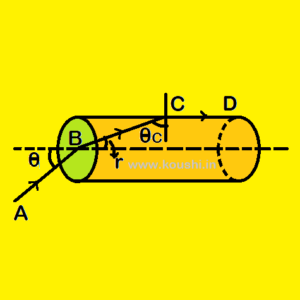
2. A cylindrical glass has refractive index ![]() is surrounded by air. A ray of light AB is incident at point B on one end of the glass as shown in figure. Determine the incident angle for which the light grazes along the surface of the glass.
is surrounded by air. A ray of light AB is incident at point B on one end of the glass as shown in figure. Determine the incident angle for which the light grazes along the surface of the glass.
Using Snell’s law at point B we get, ![]() = aµg =
= aµg = ![]() =
= ![]() —- (i)
—- (i)
As the light grazes along the surface of the glass from point C, then r + ![]() = 900.
= 900.
Using Snell’s law at point C we get, sin![]() =
= ![]()
Or, sin(900 – r) = ![]()
Or, cosr = ![]() —— (ii)
—— (ii)
From equation (i) and (ii) we get, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, 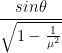 =
= ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, sin![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() = sin-1(
= sin-1(![]() ).
).
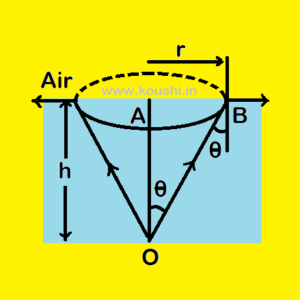
3. A fish in a water tank sees the outside world as it is at the vertex of a cone such that the circular base of the cone coincides with the surface of water. The depth of water where fish is located is h and the critical angle for water air interface is ![]() . Find the radius of the cone.
. Find the radius of the cone.
From diagram, fish is at point O and the radius of cone is AB = r.
As ![]() is the critical angle for water air interface, then sin
is the critical angle for water air interface, then sin![]() =
= ![]() .
.
From diagram, tan![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
Or, 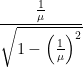 =
= ![]()
Or, ![]() =
= ![]()
![]() r =
r = ![]() .
.
Click the button to go to the next part of this chapter.
Click the button to go to the previous part of this chapter.
